A tap is a tool used for cutting threads, commonly used for machining various sizes of internal threads. When using a tap, it is important to choose the appropriate type, material, and size of the tap, as well as the correct usage method, to ensure machining efficiency and thread quality.
Tap Process
The tap process mainly includes the following steps:
Turning process: The shape of the tap is processed into a cylinder through a lathe, and the accuracy of its diameter and length is ensured.
Grinding process: Use a grinder to grind the outer surface of the tap to improve its surface roughness and roundness.
Sharpening process: The cutting part of the tap is sharpened through a sharpening machine to ensure the cutting performance and thread quality of the tap.
In addition, the production process of taps includes about 20 processes, mainly including three parts: rough machining of materials, heat treatment and finishing. The tap production equipment used for finishing is mainly a grinder, not only because of the high processing accuracy of grinding, but also because the hardness of the heat-treated tool steel is very high and can only be processed with a grinder. These tap production equipment mainly include tap square tail grinding, tap cylindrical grinding, tap groove grinding and tap thread grinding, etc.
Tap Classification:
Tap is a commonly used tool for processing internal threads. There are different types of taps according to different classification methods:
Divided according to different drives: hand taps and machine taps.
According to the processing method: cutting taps and extrusion taps.
According to the thread being processed: metric coarse thread taps, metric fine thread taps, pipe thread taps, etc.
According to their shape, they are divided into: straight flute taps, spiral flute taps and spiral point taps.
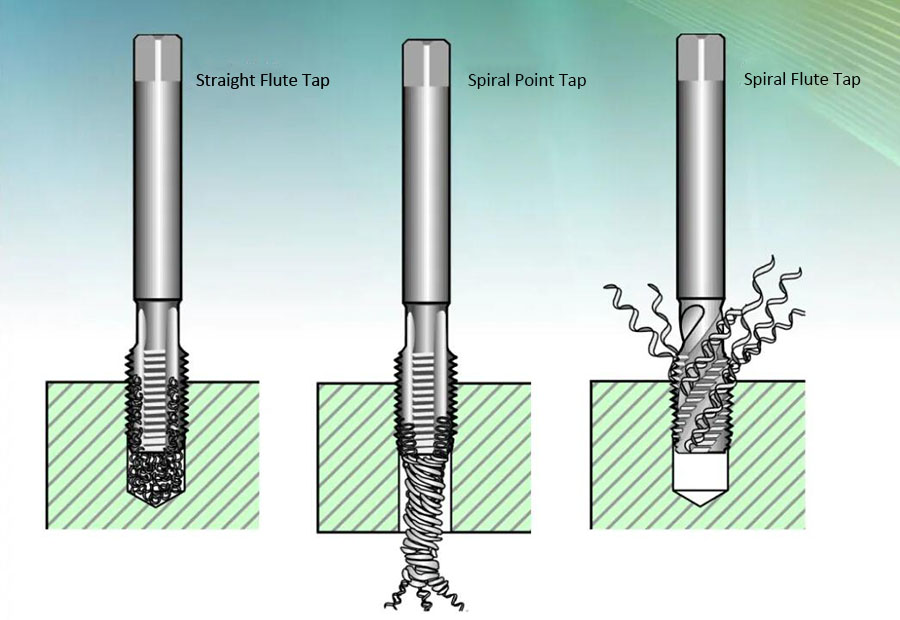
According to the tapping direction of the tap during use, it can be divided into: parallel tap and undercut tap.
Possible Problems Encountered During Tap Machining:
- Tap Breakage:
It may be caused by the selection of a small bottom hole for the thread, poor chip removal, insufficient drilling depth when the thread cannot be tapped, high cutting speed during tapping, different axes between the tapping tap and the bottom hole, inappropriate selection of tap grinding parameters, unstable workpiece hardness, and excessive wear of the tap. The solutions include: selecting the appropriate diameter of the threaded bottom hole, improving chip removal, increasing drilling depth, reducing cutting speed appropriately, correcting the fixture, increasing the lead angle of the tap, shortening the length of the cutting cone, controlling the hardness of the workpiece, selecting safety card heads, and replacing the tap in a timely manner.
- Tap Tooth Breakage:
It may be caused by excessive selection of the lead angle of the tap, excessive cutting thickness of each tooth of the tap, high tap hardness, tap wear, and other reasons. The solutions include: reducing the front angle appropriately, increasing the length of the cutting cone appropriately, reducing the hardness appropriately, and replacing the tap in a timely manner.
- Small Internal Thread:
It may be caused by incorrect tap selection, poor spindle rigidity of the machine tool, and incorrect tap tolerance selection. The solutions include: selecting the correct tap according to the processing conditions, using floating tapping threads, selecting the correct tap tolerance, etc.
- The surface roughness value of the internal thread is relatively high:
It may be caused by incorrect tap selection, high cutting speed, insufficient cutting cone length, poor chip removal, small bottom hole diameter, cold and harsh conditions, etc. The solutions include: selecting the correct tap according to the processing conditions, reducing cutting speed, increasing the length of the cutting cone, improving chip removal, controlling the hardness of the workpiece, and selecting safety clamps.
- Eccentricity of bottom hole or uneven axial feed:
Use floating thread tapping or improve the machine tool.
- Chip blockage:
Reduce the number of chip slots in the tap and expand the chip space in the chip slots; Increase and deepen the bottom hole.
- Cutting speed too high: reduce the cutting speed.
It should be noted that the specific solution needs to be analyzed and determined based on the specific problem. When performing tap machining, operators should have a high level of skill and experience in order to better deal with various problems and improve machining quality.



