Since the industrial revolution, manufacturing technology has never stopped developing. Companies are always looking for faster, cheaper or better production methods. In the past few decades, some of the most reliable processes for manufacturing custom parts belonged to two aspects: additive manufacturing or subtractive manufacturing. Materials can include plastics, thermoplastics, iron, steel, carbon, etc. Although both additive manufacturing and subtractive manufacturing processes are used to make objects from materials, they are not the same. So, what is the difference between additive manufacturing and subtractive manufacturing?
What Is Additive Manufacturing?
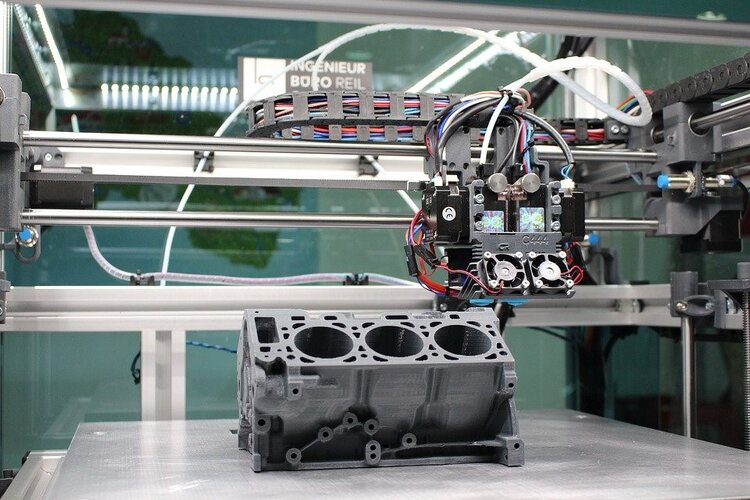
Additive manufacturing covers processes that involve the construction of objects by adding materials. When a company builds an object by adding materials to it, it is considered additive manufacturing. The material is gradually added to the bed or substrate, so that new objects with different sizes and shapes from the raw materials can be produced.
Most additive manufacturing processes involve 3D printing. In fact, the term “additive manufacturing” has become synonymous with 3D printing. A 3D printer is a machine that deposits materials on the printing bed. Therefore, they build objects by adding materials. The working principle of a typical 3D printer is to release the extruded material from the nozzle. It builds the base layer, and then builds the next highest layer. The 3D printer will continue to build each individual layer until the object is completed.
Benefit
The biggest advantage of additive manufacturing is its versatility in design. Additive manufacturing can produce highly complex models, and even designs with hollow interior parts, which other manufacturing processes cannot do. In fact, designs that can almost be created in CAD can also be replicated through additive manufacturing.
For a small number of prototype models, additive manufacturing is usually more practical. This is because additive manufacturing machines such as FDM 3D printers require very little setup. With 3D design, you can start a 3D printer in a few minutes. Since the process is almost completely automated, there is no need to spend any time making tool changes. This flexibility makes additive manufacturing the technology of choice for “on-demand” production.
Since additive manufacturing does not remove any waste from existing materials, the process inherently generates much less waste compared to subtractive manufacturing. For companies, this can reduce waste disposal or recycling costs.
Disadvantage
Although additive manufacturing is versatile in design, it is strictly limited in terms of materials. Most 3D printing technologies are limited to the use of plastic or plastic composite materials. In addition, the layer-by-layer construction method leads to structural weaknesses where the layers adhere to each other. This means that objects created using additive manufacturing may not be strong enough to support weight or withstand extreme conditions. This essentially limits the additive manufacturing used to create non-functional prototypes.
Although existing 3D printers can use metal for printing, they are still rare in the industry. Generally, using 3D printing to create custom metal parts is more expensive than using CNC machining to create custom metal parts.
Even for relatively fast 3D printing processes (such as SLS and SLA), the process of building objects layer by layer is very slow. This makes additive manufacturing impractical for responding to high-volume demand. The 3D printer also has a limited-size build platform. If the work requires large parts or models, they must be printed as smaller components and glued together. This introduces extra work, not to mention more points of failure.
What Is Subtractive Manufacturing?
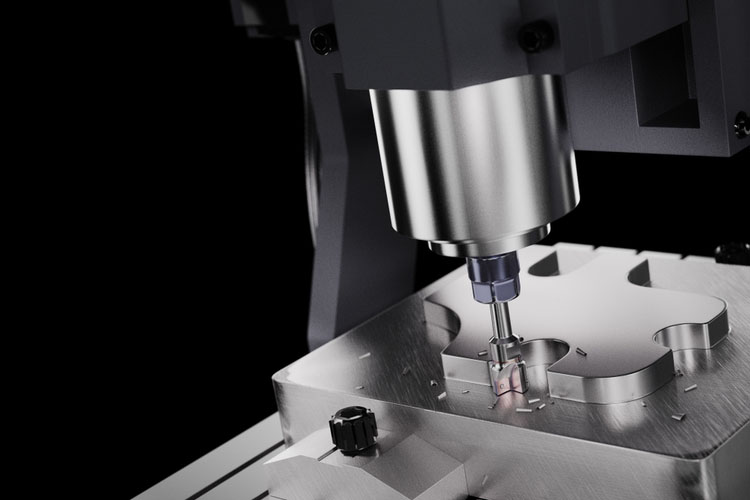

Subtractive manufacturing includes processes that involve the construction of objects by removing material. Essentially the opposite of additive manufacturing. The company does not add materials, but performs subtractive manufacturing by removing materials. It usually starts with a large piece of raw material. The company then removes the excess material from it in order to create new objects with smaller dimensions and different shapes.
The term subtractive manufacturing refers to the process of producing objects by using CNC computer numerical control (CNC) machines to continuously remove materials from the original block to achieve the desired shape and size. The process begins when the design engineer submits the CAD model to the mechanical workshop, preferably using an online quotation system. Advanced software analyzes and designs and selects tools, tool paths and best workpieces. CNC machine tools can use a variety of materials, including metal, wood, glass, ceramics, plastics and composite materials.
Advantages
Subtractive manufacturing has several key advantages:
Surface finish
High precision and geometric accuracy
Excellent repeatability
High stress applications
Compared with additive manufacturing, the cost of processing certain parts is lower. Subtractive manufacturing preserves the original integrity of the material. This means that products manufactured by subtraction are more durable, which makes the technology particularly popular in the automotive and aircraft manufacturing industries.
Compatible with multiple materials
Speed and high productivity
Subtractive manufacturing involves machines with linear and multi-axis rotation capabilities. Standard 3-axis and 5-axis CNC milling machines and lathes can machine workpieces from different directions to achieve complex designs.
The quality of models and parts created by subtractive manufacturing is generally better than that of additive manufacturing. Since this process does not produce visible layer lines, only minimal work is required in the post-processing process.
Disadvantage
It is impossible to cut or carve overly complex designs or hollow objects with CNC machining. It also takes a lot of time to set up the CNC machine. Even minor design changes may require reassembly, which must be done manually. Therefore, CNC machining is what the manufacturer reserves for mass production.
Final thoughts
In terms of manufacturing technology, additive manufacturing through 3D printing is still an emerging technology. Although its selling point is that it can create an excellent selling point for almost all 3D designs, the technology is not good enough to eliminate more traditional manufacturing methods. Subtractive manufacturing has existed for decades, but it is still widely regarded as the standard in several industries.
Subtractive manufacturing is still the method companies use when they need to produce large numbers of parts quickly and reliably. This technology is particularly suitable for manufacturing highly durable parts from metal. As more and more companies explore new technologies such as laser cutting and electrical discharge machining (EDM), subtractive manufacturing does not seem to be in any danger of disappearing.


