Computer numerical control (CNC) machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that removes material from the original block in order to achieve the required geometric specifications. The machine tool is an indispensable part of the subtractive manufacturing process, removing material through milling, grinding or drilling techniques. The machining shop uses milling and lathe tools for precision CNC machining applications to achieve the specified accuracy, tolerance and finish.
The advantage of CNC machine is that they can accommodate various cutting tools to manufacture materials of different shapes and sizes. Cutting tools can use shear deformation to rotate, cut and remove material on the workpiece. Each tool has its unique attributes and advantages. Most cutting tools have a groove, which refers to the cutting edge of the tool. The cutting edge has a spiral groove along the outer length of the tool. The tiny metal pieces cut off during processing move with the grooves when they are ejected. Different cutters have different numbers of grooves. The machinist selects the tool with the required number of blades according to the material of the workpiece and the required surface finish.
From drills and end mills to reamers, the selection of CNC machining tools is critical to obtaining the required manufacturing and finishing.
End Mill
The industry widely uses end mills for vertical CNC machining applications. Vertical machining applications create details along the surface of the workpiece, such as circular contours around edges or cutting keyways on shafts.
End mills have one or more sharp edges for various cutting and rapid removal of large amounts of material. According to its anatomy and function, there are different types of end mills. These include:
The plane end mill is a plane tool used to cut two-dimensional features on the workpiece.
Ball end mills are tools with round cutting ends, suitable for milling 3D contour surfaces.
The end mill has a flat bottom and rounded corners and is suitable for cutting round edges.
The rough machining end mill adopts a serrated design, which is suitable for quickly removing a large amount of material while leaving rough machining.
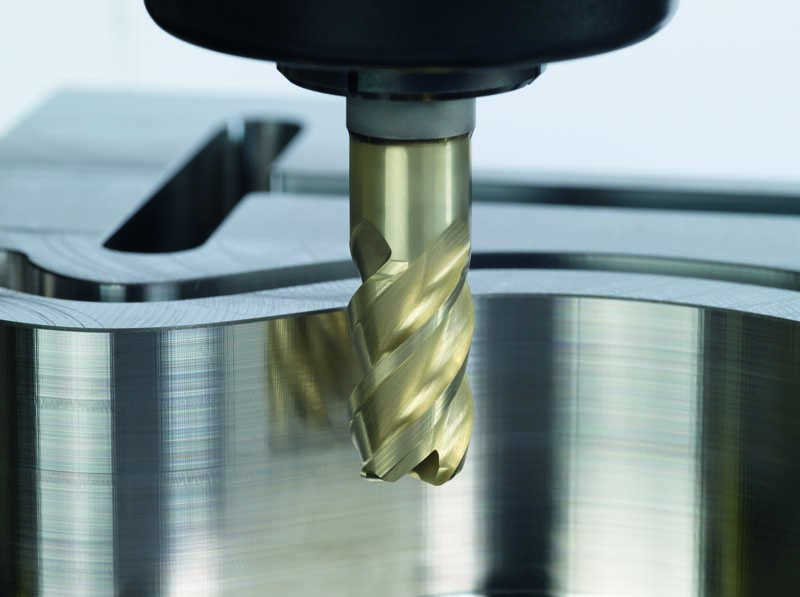
Drill
Drill bits are the most common CNC machining tool and are no different from those found in local hardware stores. They consist of a shaft with one or more chip flutes and a tapered cutting edge for rapid drilling in the workpiece. The operator matches different types of drill bits with CNC machines to perform various cutting operations.
Twist drill bit: used to drill holes in materials, most suitable for drilling holes in metal, wood and plastic.
Center bit: suitable for precise centering and drilling
Ejector bit: A tool used to drill deep holes, with a preferred diameter range of ¾ inch to 4 inches.
Thread Milling Cutter
As the name implies, thread milling cutters are tools used to cut internal or external threads in materials. Taps have a similar purpose, but they only cut internal threads. The thread milling cutter can produce threads of at least ⅛ inches (3.175 mm) until the depth of the threaded hole is approximately three diameters. Alternatively, the tap can reach a depth of up to 20 diameters. The use of large diameter tools for threading can cause CNC machines to show poor results at tap diameters of ½” (12.7 mm) or larger.
A reamer is a rotary cutting tool used in metalworking applications to drill small or deep holes, and use the oblique angle process to widen or expand the size of existing holes. The precision reamer enlarges the hole with high precision and smooths the edges, while the non-precision reamer performs basic enlargement and deburring. They are divided into single-edged reamer or multi-edged reamer according to the arrangement of the cutting edges. Single-edged reamers provide high precision and dimensional consistency to ensure accuracy, but they are expensive. The standard multi-blade reamer has multiple carbide cutting edges and round cutting edges for polishing operations. Compared with other cutting tools, mechanics prefer reamers to achieve dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances.
A hollow milling cutter is a tubular cutter with three or more cutting edges on the inner surface. It is very similar to an inverted milling cutter, and machinists use it for applications such as workpiece preparation and threading. Hollow milling cutters can perform multiple operations in one pass, such as facing, centering or chamfering. It can have 3 to 8 cutting edges, which helps to achieve relatively fast feed speeds. In this operation, the workpiece is fed into the hollow mill to produce cylindrical parts.
Bevel Gear
The bevel gear transmits the force between the two shafts at the point of intersection.
Worm Gear
It is composed of a hard metal worm with self-locking ability and a soft metal working wheel.
Used in applications that require deceleration.
The deceleration rate depends on the worm gear and the number of teeth on the worm gear.
Screw Gear
It is similar to a helical gear with a 45° tooth angle.
The carrying capacity is low.
Flying Knife
Flying knife is a single-point cutting tool, mainly used for processing large flat areas. The cutting process using a fly cutter is not as fast as a face milling cutter, but it can provide a uniform and smooth finish. The standard flying knife can be adjusted to cut aluminum up to 2 inches (51 mm) in diameter and can cut 0.0010 inches (0.25 mm) deep.
Face Milling Cutter
Before applying other milling cutters, the machine must level the workpiece to meet the design specifications. Face milling helps to prepare flat surfaces on the workpiece using various tools. The face milling cutter consists of a solid body and multiple interchangeable tool inserts. The interchangeability of the tool blades allows the cutting profile to be changed without the need to replace the entire tool. Tools at different angles produce different outputs:
10°-65° tool is a typical tool face milling application range. Manufacturers mostly use 45° tools to reduce vibration and thin chips.
The 90° tool forms a right angle. The tool is suitable for thin-walled and weakly fixed parts.
Large radius or round insert milling cutters, shoulder milling cutters, side milling cutters and face milling cutters are suitable for various operations from demanding complex face milling to simple profiling.
Determine Which Tools Your CNC Machining Application Needs
The machining workshop uses advanced software to select the appropriate tools for use with the CNC machine to manufacture the final product with the required specifications. A typical machining shop has a rich tool library and can choose to order special tools when needed. Each manufactured part has a unique geometric shape, and the workshop can analyze it manually or using proprietary software to select the best tool.


