Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating has become one of the most valuable surface-enhancement technologies in modern engineering, especially for CNC-machined components that require exceptional wear resistance, low friction, and long-term durability. Known for its unique combination of hardness, chemical stability, and smoothness, DLC provides performance benefits that far exceed those of traditional plating or anodizing methods. As industries continue to demand lighter, faster, and more efficient mechanical systems, DLC coating has evolved into a critical finishing solution for high-precision metal parts.
DLC Coating: What Makes It Special?
DLC refers to a family of amorphous carbon coatings that mimic key properties of natural diamond. These coatings are typically applied using processes such as Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD), creating an ultra-thin, extremely hard layer on the surface of the part. The resulting film delivers exceptional hardness—often exceeding 2,000 HV—combined with extremely low friction coefficients, typically around 0.1 or even lower.
Unlike conventional coatings such as chrome plating or nitriding, DLC provides a balance of mechanical strength and surface smoothness while maintaining minimal coating thickness. This makes it particularly suitable for CNC-machined parts with tight tolerances, where dimensional accuracy and surface functionality are critical.
Types of DLC Coating
There are several types of DLC coatings, each designed for different applications. The main types include:
- Hydrogenated DLC (a-C:H) – Common and versatile, used in automotive and mechanical parts.
- Non-Hydrogenated DLC (a-C) – Very hard, often used in high-performance tools.
- Tetrahedral Amorphous Carbon (ta-C) – The hardest form of DLC, closest to diamond in properties.
- Metal-Doped DLC (Me-DLC) – Mixed with metals like tungsten or titanium for special friction and wear performance.
Choosing the right type depends on the application, operating environment, and material of the base part.
Performance Advantages for CNC Machined Parts
The primary reason engineers choose DLC coating is its ability to significantly enhance the performance of high-precision machined components. The coating dramatically reduces wear, extending the lifespan of moving or sliding parts even under aggressive mechanical loads. Low friction reduces heat generation and allows components to operate more efficiently at higher speeds—an important benefit in aerospace, automotive, and high-performance machinery.
DLC also provides outstanding resistance to corrosion and chemical exposure. It prevents oxidation on steel components, protects against aggressive lubricants, and withstands exposure to moisture and environmental contaminants. Combined with superior scratch resistance and excellent fatigue performance, these characteristics enable CNC-machined parts to maintain stability and reliability even under long-term cyclic loading.

Ideal Applications in Precision Manufacturing
Industries that require dependable mechanical performance at high speeds or within abrasive environments often rely on DLC-coated parts. In automotive systems, DLC is commonly applied to camshafts, fuel injection components, piston pins, and transmission parts to reduce friction and decrease energy losses. Aerospace applications include actuators, valves, and critical linkage components that operate under variable loads and fluctuating temperatures.
In robotics and automation, DLC-coated shafts, gears, and bearings benefit from reduced maintenance requirements and extended operational cycles. High-end consumer electronics also use DLC for enhanced wear protection on sliding assemblies, buttons, and frames. Even in medical devices, DLC offers biocompatibility and sterilization resistance, making it suitable for surgical tools and implantable components.
CNC Machining and Surface Preparation for DLC Coating
Successful DLC coating begins with precision CNC machining. Because DLC layers are extremely thin, the surface finish and geometry of the machined component must already meet performance requirements. Any machining marks, burrs, or surface imperfections will transfer through the coating and impact the final part’s functionality.
For this reason, DLC-coated parts often require additional finishing steps such as polishing, micro-deburring, or fine grinding before the coating process. Materials such as stainless steel, tool steel, titanium, and aluminum alloys respond particularly well to DLC, though some substrates require an intermediate layer to ensure proper adhesion. Temperature control is also critical, as DLC processes can expose parts to elevated temperatures that must not affect the underlying material properties.
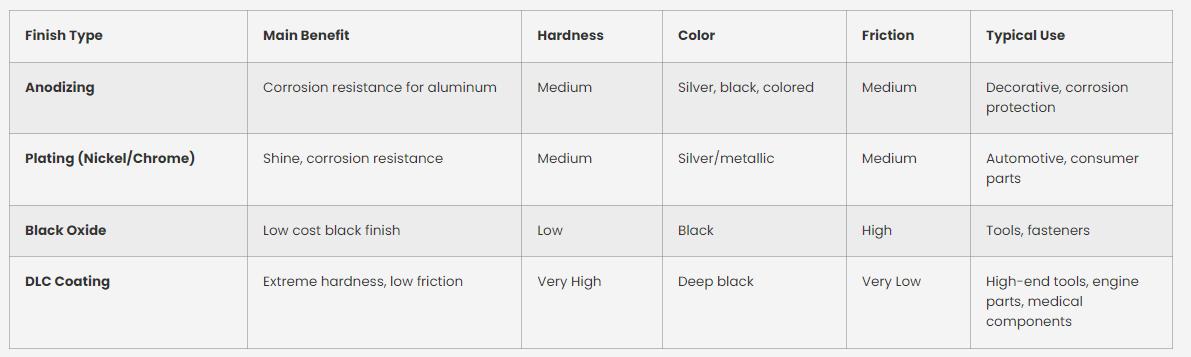
DLC Coating vs Other Surface Treatments
While many surface treatments improve the durability and performance of CNC-machined parts, DLC coating offers a unique combination of properties that often outperforms traditional methods. Compared with hard chrome plating, DLC provides significantly higher hardness and dramatically lower friction without the environmental concerns associated with hexavalent chromium. When compared with nitriding, DLC forms at lower temperatures, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials while still delivering superior wear and fatigue resistance. Surface finishes such as anodizing or nickel plating improve corrosion resistance, but they cannot match the extreme hardness and lubricity of DLC. Even advanced coatings like TiN or TiCN used in cutting tools tend to exhibit higher friction coefficients and less versatility across materials.
DLC stands out because it delivers a balanced combination of hardness, low friction, chemical resistance, and thin-film uniformity, allowing precision tolerances to remain intact. This makes it particularly advantageous for components that operate under sliding contact, high-speed conditions, or environments where long-term reliability is essential. Although DLC may have a higher application cost than traditional coatings, its extended service life and performance advantages often result in lower total cost of ownership.
Why Manufacturers Choose DLC for High-Precision Components
As industries evolve toward higher efficiency and reduced environmental impact, DLC coating has become more attractive due to its ability to improve performance without increasing lubricant consumption or requiring frequent part replacement. The combination of exceptional wear resistance, corrosion protection, and ultra-low friction makes DLC one of the most versatile surface technologies available for CNC-machined parts.
For manufacturers seeking to elevate product quality, minimize failure risks, and deliver long-lasting performance, DLC offers a proven, high-value solution. Whether applied to critical engine components or delicate surgical instruments, DLC coating empowers CNC-machined parts to perform reliably under the most demanding conditions.



