In high-performance industries such as aerospace, energy, and automotive, components are often exposed to extreme temperatures that can weaken conventional materials. This is where heat-resistant metals play a crucial role. Their ability to maintain mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures makes them indispensable in precision CNC machining.
This article explores the top five heat-resistant metals commonly used in CNC machining — their properties, advantages, and ideal applications.
1. Titanium Alloys
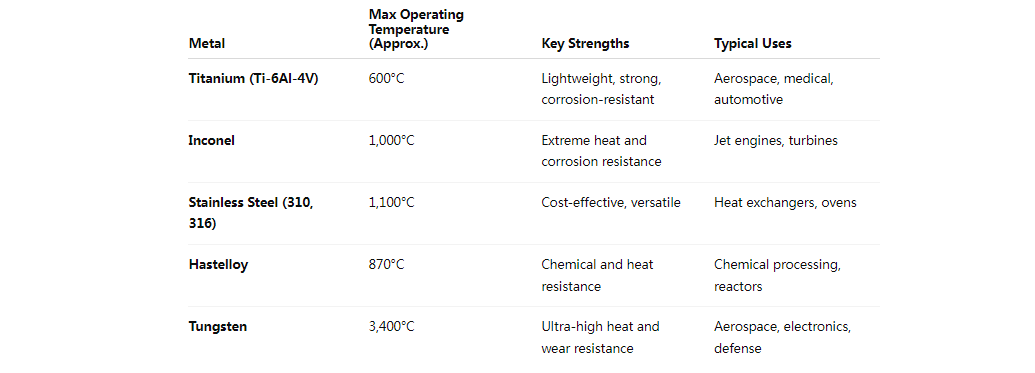
Titanium is one of the most well-known high-temperature materials used in modern manufacturing. Titanium alloys, especially Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), are prized for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to retain mechanical integrity at temperatures up to 600°C (1,112°F).
Key Benefits
- Outstanding heat and corrosion resistance
- High specific strength (ideal for lightweight designs)
- Excellent biocompatibility (used in medical and aerospace fields)
CNC Machining Notes
Titanium is notoriously difficult to machine because of its low thermal conductivity — heat accumulates at the cutting zone, leading to tool wear. To achieve optimal results, machinists use carbide tools, high-pressure coolant, and optimized cutting speeds.
Common Applications
- Aerospace turbine components
- Automotive exhaust systems
- Medical implants and prosthetics
- Marine and chemical processing equipment
2. Inconel (Nickel-Based Superalloy)
Inconel is a family of nickel-chromium-based superalloys that can withstand extreme temperatures exceeding 1,000°C (1,832°F) while retaining remarkable strength. Its microstructure remains stable even under heavy mechanical and thermal stress, making it a top choice for demanding environments.
Key Benefits
- Exceptional oxidation and corrosion resistance at high temperatures
- Maintains strength and hardness under thermal cycling
- Excellent creep and fatigue resistance
CNC Machining Notes
Inconel is challenging to machine due to work hardening and low thermal conductivity. Successful machining requires rigid setups, sharp tools, and controlled feeds to avoid overheating. CNC turning and milling of Inconel typically involve nickel-specific cutting fluids and multi-step finishing to achieve tight tolerances.
Common Applications
- Gas turbine blades and combustion chambers
- Jet engine exhaust systems
- Nuclear reactor components
- Oil and gas drilling equipment
3. Stainless Steel (Grade 310 and 316)
While stainless steels are often associated with corrosion resistance, certain grades, like 310 and 316, also deliver outstanding heat resistance.
Grade 310 stainless steel, for example, contains a high percentage of chromium and nickel, which enhances oxidation resistance at temperatures up to 1,100°C (2,010°F). Grade 316 combines strong corrosion resistance with moderate high-temperature strength, making it a popular all-around material.
Key Benefits
- Excellent resistance to oxidation and scaling
- Good strength at elevated temperatures
- Widely available and cost-effective
CNC Machining Notes
Stainless steels are easier to machine than superalloys, though work hardening can still occur. Using sharp tools, coolant, and consistent feed rates ensures smooth machining and fine surface finishes.
Common Applications
- Heat exchangers and boilers
- Exhaust manifolds
- Industrial ovens and kilns
- Marine components and fasteners
4. Hastelloy
Hastelloy, another nickel-based alloy, is engineered for corrosive and high-temperature environments. Known for its stability under both oxidizing and reducing conditions, Hastelloy maintains strength up to 870°C (1,600°F) and resists pitting, stress-corrosion cracking, and crevice corrosion.
Key Benefits
- Superior resistance to acids and chemical corrosion
- Excellent performance in high-temperature, high-pressure environments
- Long-term stability under thermal cycling
- CNC Machining Notes
Machining Hastelloy requires rigid tooling setups and moderate cutting speeds to control heat buildup. It tends to work-harden quickly, so consistent cutting pressure and coolant are critical.
Common Applications
- Chemical processing plants
- Heat exchangers and reactors
- Aerospace engine components
- Marine and defense systems
5. Tungsten and Tungsten Alloys
Tungsten is one of the highest melting point metals, withstanding temperatures above 3,400°C (6,152°F) — making it ideal for extreme heat applications. Its density, hardness, and thermal conductivity make it suitable for precision CNC machining in defense, aerospace, and electronics.
Key Benefits
- Exceptional heat resistance and melting point
- Excellent dimensional stability at high temperatures
- Superior wear resistance
CNC Machining Notes
Due to its hardness and brittleness, tungsten can be difficult to machine. Carbide or diamond tooling, low cutting speeds, and coolant control are essential to avoid cracking or tool damage. Tungsten alloys like Tungsten-Copper and Tungsten-Nickel-Iron improve machinability while maintaining heat tolerance.
Common Applications
- Rocket nozzles and heat shields
- Electrical contacts and radiation shielding
- Tooling for high-temperature die casting
- Aerospace propulsion systems
Choosing the Right Heat-Resistant Metal
Choosing the best heat-resistant material depends on your specific application and machining priorities.
- What’s the maximum operating temperature?
If temps exceed 1,000°C, go for Inconel or Hastelloy. Under 700°C? Tool steel or stainless may be enough.
- Is corrosion also a factor?
Titanium and Hastelloy don’t just stand up to high temperatures, they also offer excellent protection against harsh chemicals, making them ideal for more demanding environments.
- Is weight a concern?
Titanium is unbeatable for high strength-to-weight requirements.
- Do you need machinability or extreme strength?
Stainless steel and tool steel offer easier CNC processing than exotic alloys like Inconel or Hastelloy.
Here’s a quick summary:
Conclusion
Heat-resistant metals are the backbone of high-performance manufacturing, where durability, safety, and precision are non-negotiable.
Among them, titanium, Inconel, stainless steel, Hastelloy, and tungsten stand out as the top performers for CNC machining. Each offers a unique balance of strength, heat tolerance, and machinability, ensuring reliable performance under the most demanding conditions.
Whether you are designing turbine components, medical devices, or industrial machinery, selecting the right heat-resistant metal can mean the difference between operational success and premature failure. With modern CNC technology, these advanced materials can now be machined with remarkable precision, making them the foundation of next-generation engineering solutions.



